
updated the 28.04.2025
Understanding the European Sustainability Reporting Standards
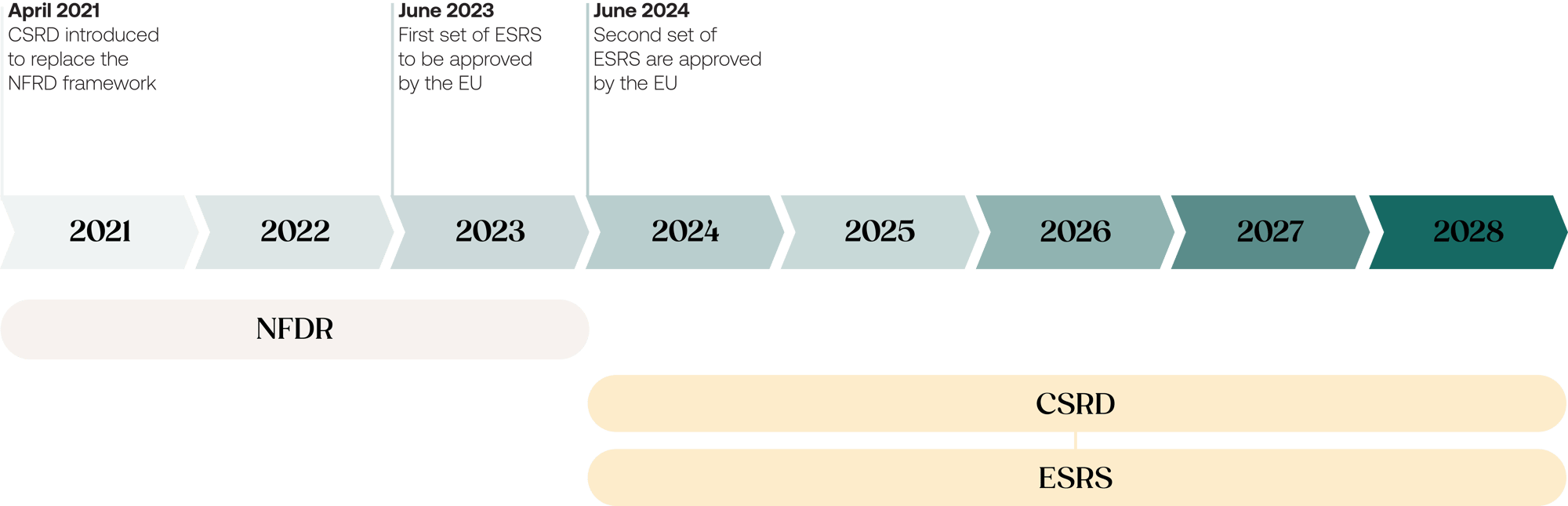
The ESRS are the detailed framework that companies must use to report on sustainability performance, as required by the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). While the CSRD sets the general guidelines for sustainability reporting, the ESRS outlines the specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and data points that need to be included in company reports. These standards ensure that sustainability is measured consistently, making the information more reliable and comparable across the EU.
Companies already have much of the necessary information for reporting, but the ESRS introduces new areas for disclosure. These include both quantitative data and qualitative descriptions that must be included in the annual report. This provides a structured approach to sustainability, moving away from the previous free interpretation of sustainability practices. The ESRS brings clarity and uniformity to how businesses report, ensuring all companies follow the same criteria, regardless of industry.
Companies already have much of the necessary information for reporting, but the ESRS introduces new areas for disclosure. These include both quantitative data and qualitative descriptions that must be included in the annual report. This provides a structured approach to sustainability, moving away from the previous free interpretation of sustainability practices. The ESRS brings clarity and uniformity to how businesses report, ensuring all companies follow the same criteria, regardless of industry.
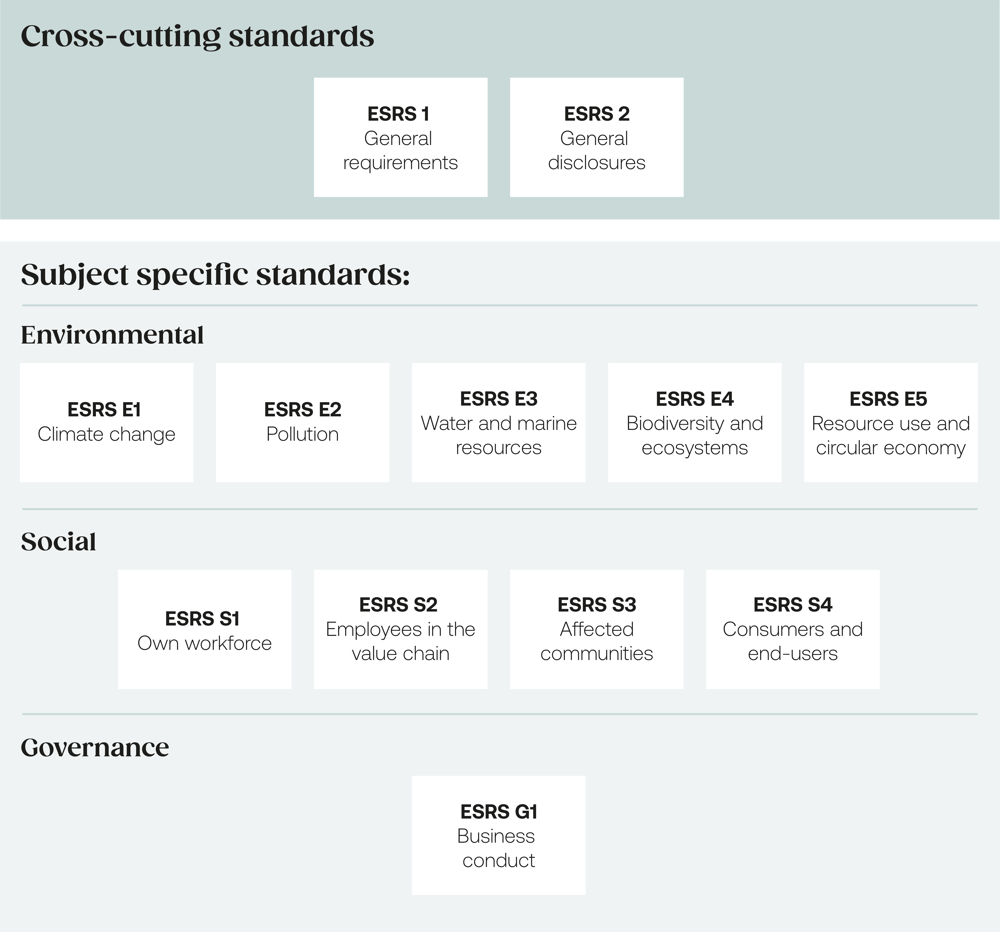
The twelve ESRS
The ESRS includes 12 reporting standards. Two of these are mandatory for all companies complying to the CSRD. The other 10 topic-specific standards are dependent on the company's double materiality assessment, meaning companies report based on the relevance of these topics to their business activities.
These standards provide not only a framework for compliance but also a tool for businesses to assess and communicate their sustainability performance effectively, which will become increasingly important in supply chain management and partnerships.
These standards provide not only a framework for compliance but also a tool for businesses to assess and communicate their sustainability performance effectively, which will become increasingly important in supply chain management and partnerships.
Does the European Sustainability Reporting Standards affect your company?
The ESRS is not a stand alone reporting regulation but serves as a detailed framework that shapes how sustainability information should be reported. This means it becomes applicable for your company when you begin your reporting obligations, which you can learn more about here.
